COVID-19
COVID-19 was first identified in December 2019 and was declared a global pandemic within months. It became the second-leading cause of death in 2021, causing a global decline in life expectancy.
Photo by Alisha Jucevic, Reuters.
Key findings
We began forecasting the trajectory of the COVID-19 pandemic in early 2020 to help hospitals and policymakers plan how to allocate resources. Now, we estimate cases, deaths, and disability due to COVID-19 as part of the Global Burden of Disease study.
Life expectancy declined in 84% of countries and territories during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Between 1950 and 2021, global life expectancy increased by almost 23 years from 49 to 71.7 years. But it declined by 1.6 years between 2019 and 2021.
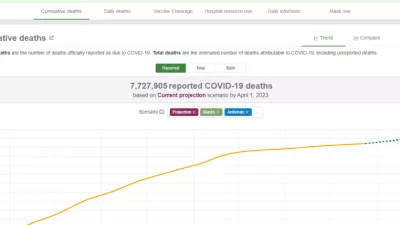
Women are twice as likely as men to develop long COVID.
On average, long COVID lasts nine months for someone who was hospitalized for their illness and four months for someone who was not.
15% of those with long COVID symptoms three months after becoming infected with COVID continued to experience symptoms even at 12 months.
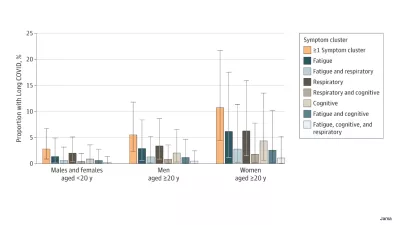
US states that imposed more vaccine and mask mandates had lower infection rates.
However, there were trade-offs that came with those decisions. While states with more restrictions did not experience worse economic outcomes, they did have lower rates of employment and lower student test scores.
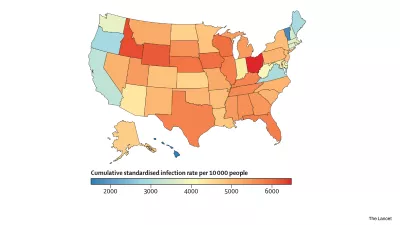
3 million people died from COVID-19 in 2022.
In December 2022, we paused our regular COVID-19 updates. Past estimates remain publicly available in our interactive data visual.